ESR Value Chart - Equivalent Series Resistance value table chart
Remember that low ESR is always better
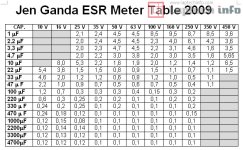
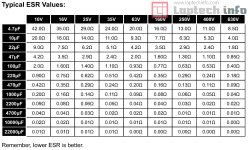

Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) is a measure of the internal resistance of a capacitor or inductor, representing the resistance in series with the ideal capacitance or inductance. It's a crucial parameter for understanding component behavior, especially in high-frequency and power applications, as it affects energy dissipation and overall circuit performance.
Key points about ESR:
- Non-ideal components:
Capacitors and inductors are not perfectly ideal; they have some internal resistance that impacts their performance.
- Energy dissipation:
ESR causes energy to be dissipated as heat, which can be detrimental to circuit operation, especially in high-power applications.
- Impact on circuit behavior:
ESR affects the capacitor's impedance and how it responds to voltage and current changes, particularly at higher frequencies.
- Lower ESR is generally better:
In most applications, a lower ESR leads to better performance, especially in power supplies and high-frequency circuits, as it minimizes energy loss and heat generation.
- Energy dissipation:
- Understanding capacitor behavior:
ESR helps predict how a capacitor will behave in a circuit, including its charging and discharging characteristics.
- Improving circuit performance:
By understanding and managing ESR, engineers can optimize circuit design to minimize energy loss and improve stability.
- Troubleshooting:
ESR measurements can be used to diagnose capacitor issues, as a high ESR can indicate a failing or degraded capacitor.
- Understanding capacitor behavior:
