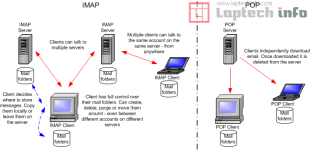
The primary distinction between IMAP and POP is how messages are sent and how long they are retained on the mail server.
POP – Post Office Protocol
When POP is utilized, messages are “pulled down” from the mail server; depending on how your email program is configured, they may or may not be erased from the server during or after this process. Messages are often erased from the server immediately or after a certain time period, such as 10 days, after being “POPed” to your email client.This implies that your emails are only accessible from the computer or device on which they were downloaded (unless you have specifically configured each device’s email program to “leave a copy of the email on the server”).
In this regard, if the computer or gadget that has downloaded all of your emails decides to go extinct, or worse, is stolen, all of your history emails will be lost – unless, of course, you have created file backups, which you have, haven’t you?!!!
While POP saves your hosting server’s disk resources (less space is taken up by saved, old emails that are downloaded instead), it generally restricts how you access your email. One advantage of POP over IMAP is that it does not require a persistent connection to the email server while the email is being viewed.
IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol
When IMAP is used, messages are often stored permanently on the mail server, but the “header” and “content” of messages are delivered to email clients (for example, your phone, desktop email program such as Outlook, or your smart TV!). This implies they can be accessed from any number of computers or devices as long as the user enters the relevant login details. In other words, all of your devices that are linked to the email server using IMAP, such as your PC, tablet, and phone, will “mirror” each other in terms of email. In this regard, deleting a message on your computer email software, for example, deletes it from your phone and the server, and vice versa.IMAP is often seen as convenient because it allows you to access the same inbox or outbox from multiple devices. However, IMAP often requires more dedicated disk space because messages are not downloaded or destroyed in the same way that POP messages are. As a result, IMAP is fantastic as long as users monitor their disk usage and continue to delete old or undesired communications as needed. It’s also important to remember that IMAP requires a persistent connection to the email server while an email is being viewed, so it’s not ideal for users who frequently go offline for extended periods.
SMTP: SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a set of standard Internet procedures by which two email providers (example. Gmail, Yahoo Mail), transfer email messages to one another’s mail servers.
Domain: A domain is a name for an IP address and is more commonly recognized as a website or web address. For example, Google.com is a domain.
SSL: SSL (secure socket layer) is a way of changing data such as your username and password into code as it travels across the Internet, so that the data will be secure and private. An SSL certificate must be installed on the server in order to protect a website with HTTPS and indicate a secure site.
ISP: An ISP (Internet Service Provider) is a company (ex. Airtel, BSNL, and AT&T) that gives your computer Internet access. ISPs are usually the companies that come to your house and set up all the wires.
TLS: TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a way of changing data such as your username and password into code as it travels across the Internet, so that the data will be secure and private. With mail delivery, TLS begins with an unsecured connection to the mail servers, and then upgrades to a secure connection once information is sent.
POP: POP (Post office protocol) is a one-way download of your messages that allows you to access your mail with a mail program like Outlook Express or Apple Mail. POP only offers one-way communication, which means that actions you take in the mail program (like marking a message as read) won’t be synced to Gmail. In addition, if you choose not to keep a copy on the server, all of your email would be lost if your computer malfunctioned, since it is stored locally. We recommend regular backups AND IMAP instead!
IMAP: IMAP (Internet message access protocol) lets you download messages from the Purple Dog Server (or Gmail if you are using that service) so you can access your mail with a program like Outlook Express, Apple Mail or Thunderbird. IMAP syncs the actions you take in your email client with the server so if you read a message in your mail client, it’ll be marked as read on the server (or in Gmail). Also, if your computer malfunctions, your email still exists on the server, so long as you haven’t deleted it. Furthermore, you can access your email from a wide range of devices, all using IMAP and all reflecting the same message status (e.g. read, junk, sent)
G-Mail: Gmail is a free web based email utility provided by Google. we recommend using Gmail in conjunction with IMAP on your local machine for best email results. It can be a bit complicated to set up – but once its done, you shouldn’t ever have to worry about email set up issues again.